How to Determine Which Polymer Is Used for a Molecule
Mn FW end groups FW repeating unit n 5506 7160 4405 869 509. Calculate the degree of polymerization of a sample of polyethylene CH2-CH2n which.

Determination Of The Molecular Weight Of A Polymer Via Oswald
Polymers that have a positive charge otherwise known as cationic and a high molecular weight are typically used for thickening and dewatering solids separation processes.
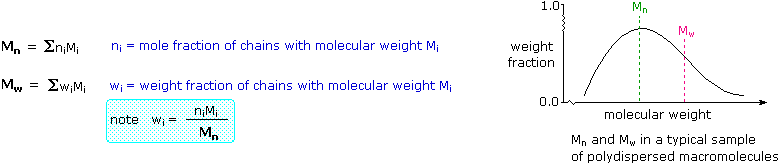
. A polymer molecule is a molecule that contains a sequence of at least 3 monomer units which are covalently bound to at least one other monomer uni t or other reactant. JOURNAL OF APPLIED POLYMER SCIENCE VOL. The amount of polymer molecules presenting the same molecular weight must be 50 of the weight of the substance.
Thus polytetra uoroetheylene is a polymer made by polymerizing tetra uoroethylene monomers. Sensitivity of the instrument and the subsequent ability to detect end. All from Polymer Literature Polymers July 22 2020 September 11 2021 The Degree of polymerization DP or Xn is defined as number of repeating monomer units in the polymers.
The most common technique that is used to determine the average molecular weight of a polymer is the viscometry where Ubbelohde viscometer is employed. A sharp molecular weight distribution peak indicates a sample that has mostly one narrow molecular range also known as a monodisperse sample. In end group analysis we use 1 H NMR measurements to determine the ratio of a specific proton in the repeat units to a specific proton in the end group.
Polymers can have different charges charge densities and molecular weights. The degree of polymerization DP or number of repeating units can be determined by comparing in the 1D 1H spectra the integral of the end. Scientists at Sigma-Aldrich routinely determine number-average molecular weight M n by 1 H NMR end-group analysis for polymers having M n values under 3000.
Im sorry im not too sure what you mean by how long is 1 mole if its 1 molecule. The molecular weight of the polymer is measured by using viscometer and the molecular weight obtained by this technique is called viscosity average molecular weight. In the context of this definition.
The molecular weight of the polymer solution is very high so the viscosity of polymer solution is very high compared to that of pure solvent. Polymers are long chain molecules produced by linking small repeat units monomers together There are many ways to link different types of monomer to form polymers Polymers exhibit very different physical properties compared to the monomers dependent on the length of the polymer chains The presence of small amounts of very long or very short chains can have. Remember the end group might be something like the.
An example is the use of a monofunctional amine in place of the dia-mine in the preparation of nylon-66 Figure 21C. Determination of the molecular weight of polymers by end-group analysis. For example if a polymer contains 13.
Polymer dose is measured in lbs. At least two SAXS curves are required to determine the molecular weight of a polymer. One of the main parameters determining the properties of a polymer is the degree of polymerization which is directly related to the molecular weight.
A very common example of the kind of measurement widely used to determine M n today is end group analysis. N sum of CH2 proton integrals of CH2 protons integral per proton value 2079 151874497 869 repeating units n. Of polymer per dry ton of solids Polymer Dose lbston 2000 x P x p F x f Where P Polymer Rate gpm p Polymer Concentration polymer product F Sludge Feed Rate gpm f Sludge Feed Concentration sol or volume in mL for lab testing.
Important analytical considerations for MS analysis of polymers. In this method the polymer should be in liquid form. The solution should be dilute enough to avoid spatial correlation effects.
If a polymer is made from more than one type of monomer or has more than a. M is the molecular weight of the polymer DP is the degree of polymerization and the M 0 is the formula weight of the repeating unit. 1 basepair has a length of 0034nm.
In my opinion the best way to determine the molecular weight of a polymer is GPC gel permeation chromatography. Trifunc-tional monomers can be used to create crosslinked polymers ie thermosets as will be. M DP M0.
1 molecule of DNA has 220x106 base pairs in 1 mol there would be 220x106 x 602 x1023 1324 x 1032 base pairs. Polymer 2 Mw 64 200 144 8 20 12 102 Small variations in the low Mw area will affect Mn but not Mw Mz. A Depiction of a Floc Formed by a Cationic Polymer Chain Bridging the.
A broad molecular weight distribution peak indicates that there are many different molecules with different molecular weights that the sample is very polydisperse. Average molecular weight determined by MS will not give. If not it has to be dissolved using a.
21 1977 Estimation of Molecular Weight by Gel Permeation Chromatography and Viscometry A calibration curve ie the relationship between molecular weight and elution volume is necessary to calculate average molecular weights of polymer samples from GPC data. The Degree of a polymerization is calculated by taking ratio of molecular weight of the polymer and molecular weight of the repeat unit. Sometimes a monofunctional mono-mer may be a d d e d during the polymerization process to control molecular weight.
The SAXS procedure to determine the molecular weight of polymer sample in monomeric or multimeric state solution requires the following conditions. Theyre not used very often anymore. Length of 1 mol of DNA would be 1324 x 1032 x 0034 nm 450 x 1021 m.
In addition NMR analysis can also be used to accurately determine monomer ratios for various copolymer molecules. Small variations in the high Mw area will affect Mz1 Mz Mw but not Mn. In most cases you use polystyrene standards to.
The system should be monodispersed. The composition of the whole sample free of water salts and additives is defined by Acetate butyrate AGU 100. If a polymer is made from only one type of monomer or if it has a single repeat unit it is called a homopolymer.
Polymers often indicate the starting monomer material.

Polymerization Definition Classes Examples Britannica

Determination Of Molecular Weight Of Polymers Introduction Molecular
No comments for "How to Determine Which Polymer Is Used for a Molecule"
Post a Comment